.jpg)
Overview
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is a noble gas and is the third-most abundant gas in the Earth's atmosphere, making up about 0.934% by volume. Argon gas is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and non-toxic.
- Discovery and Isolation Argon was first reported by Lord Rayleigh and Sir William Ramsay in 1894. They discovered the element while trying to isolate a new component from the air. They found that argon was present in the air in small amounts and was not reactive.
- Production Argon is produced through the fractional distillation of liquid air. It is obtained commercially by the distillation of liquid air, which separates the gases by their boiling points. Argon is also produced by the decay of potassium-40 in the Earth's crust.
- Properties Argon is a noble gas and is chemically inert. It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, and non-toxic. Argon gas is denser than air and is about 1.4 times as heavy as air. It has a boiling point of -185.9°C (-302.6°F) and a melting point of -189.3°C (-308.7°F).
Use
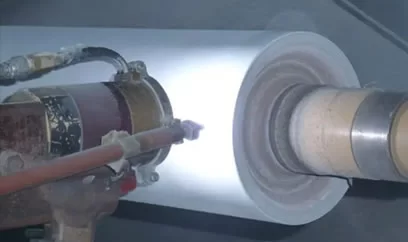
Argon gas is used in medical applications, such as in laser surgery and cryosurgery. In laser surgery, argon gas is used to cool the laser and prevent damage to surrounding tissue. In cryosurgery, argon gas is used to freeze and destroy cancerous tissue.
Conclusion
Argon gas is a versatile and important gas that has many uses in various industries. From welding and metal fabrication to lighting and medical applications, argon gas plays an important role in many processes and products. With its many properties and applications, argon gas is a valuable resource that will continue to be used for years to come.
Applications

Electrical Welding

Glass

Steel
Medical

Wines